| Era The Renaissance (1400 – 1600) |
| Alternative Names 15th and 16th Centuries |
| Total Entries 46 |
| Articles Renaissance – Wikipedia Elizabethan era – Wikipedia English Renaissance theatre – Wikipedia |
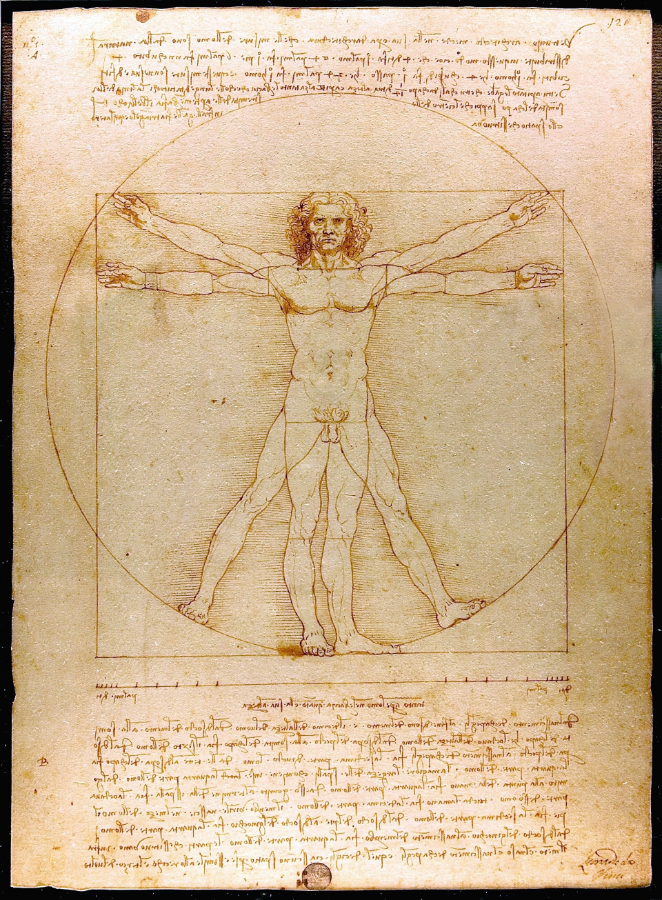
| Description The Renaissance included Gutenberg’s invention of the printing press in 1440, eventually followed by printed editions of Dante’s Divine Comedy in 1481, widely-shared. The era is highlighted by the work of Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) and Michelangelo (1475–1564). Libraries opened to the public. The importance of education increased. Every continent was visited and mapped. Elizabethan theatre became a distinctive style via Shakespeare (1564–1616) and his contemporaries.
The Renaissance is a… European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including art, architecture, politics, literature, exploration and science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the rest of Italy and later throughout Europe… The Renaissance’s intellectual basis was founded in its version of humanism, derived from the concept of Roman humanitas and the rediscovery of classical Greek philosophy, such as that of Protagoras, who said that “man is the measure of all things”. Although the invention of metal movable type sped the dissemination of ideas from the later 15th century, the changes of the Renaissance were not uniform across Europe: the first traces appear in Italy as early as the late 13th century, in particular with the writings of Dante and the paintings of Giotto. As a cultural movement, the Renaissance encompassed innovative flowering of literary Latin and an explosion of vernacular literatures, beginning with the 14th-century resurgence of learning based on classical sources, which contemporaries credited to Petrarch; the development of linear perspective and other techniques of rendering a more natural reality in painting; and gradual but widespread educational reform. It saw myriad artistic developments and contributions from such polymaths as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo, who inspired the term “Renaissance man”… ~ Renaissance – Wikipedia
|