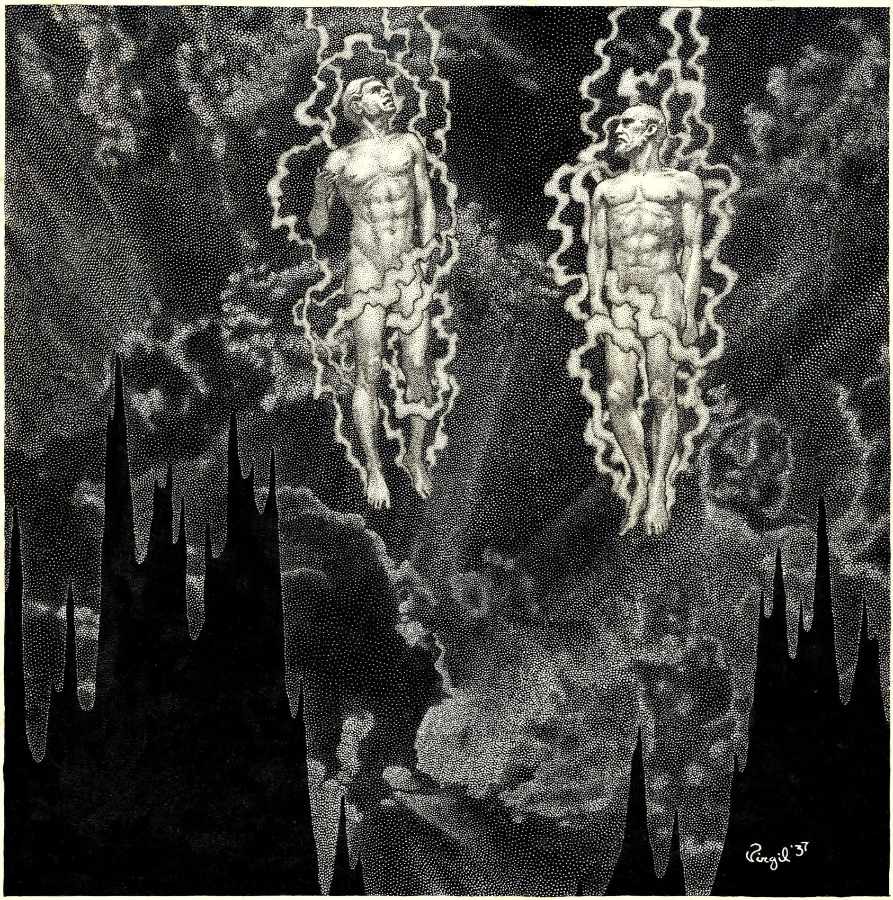| Era Modernism Era (1914 – 1937) |
| Alternative Names Elite Modernism, Radium Age (1904-1933), Expressionism, Futurism, Vitalism |
| Total Entries 210 |
| Articles “Metropolis (1927): City, Cinema, Modernity” by Anton Kaes – Weimar Cinema: An Essential Guide to Classic Films of the Era (2009) Scorched Earth: Expressions of Modernity in Dashiell Hammett’s Pulp Fiction – Anna P. Kelly via Harvard.edu H. P. Lovecraft and the Modernist Grotesque – Sean Elliot Martin via Duquesne.edu |
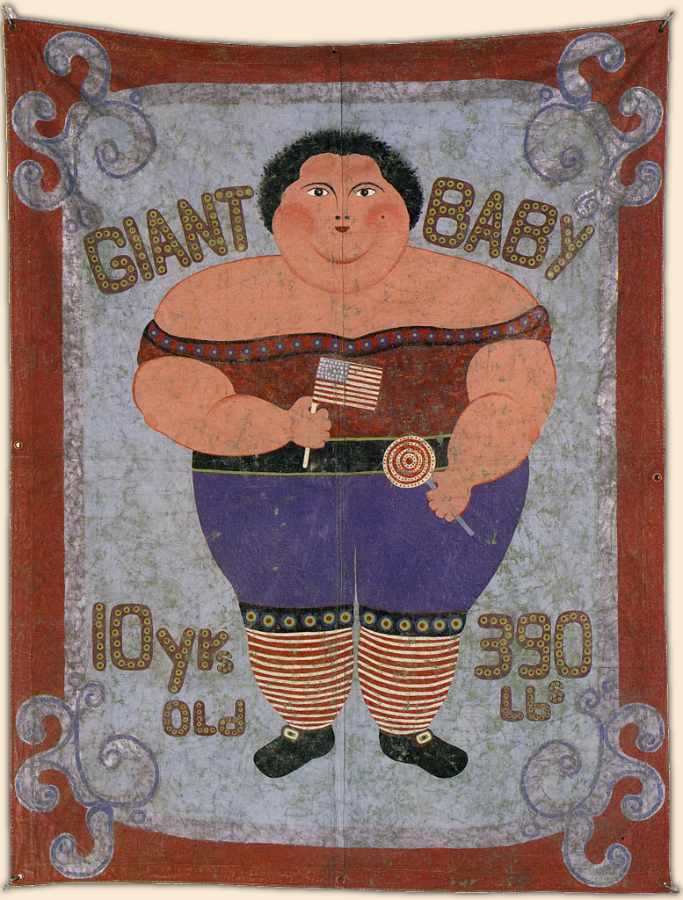
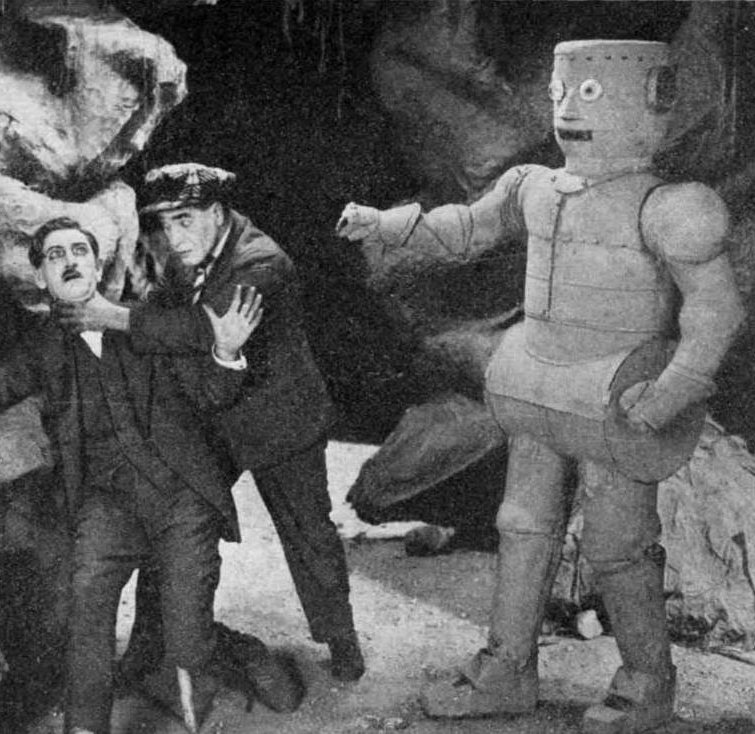
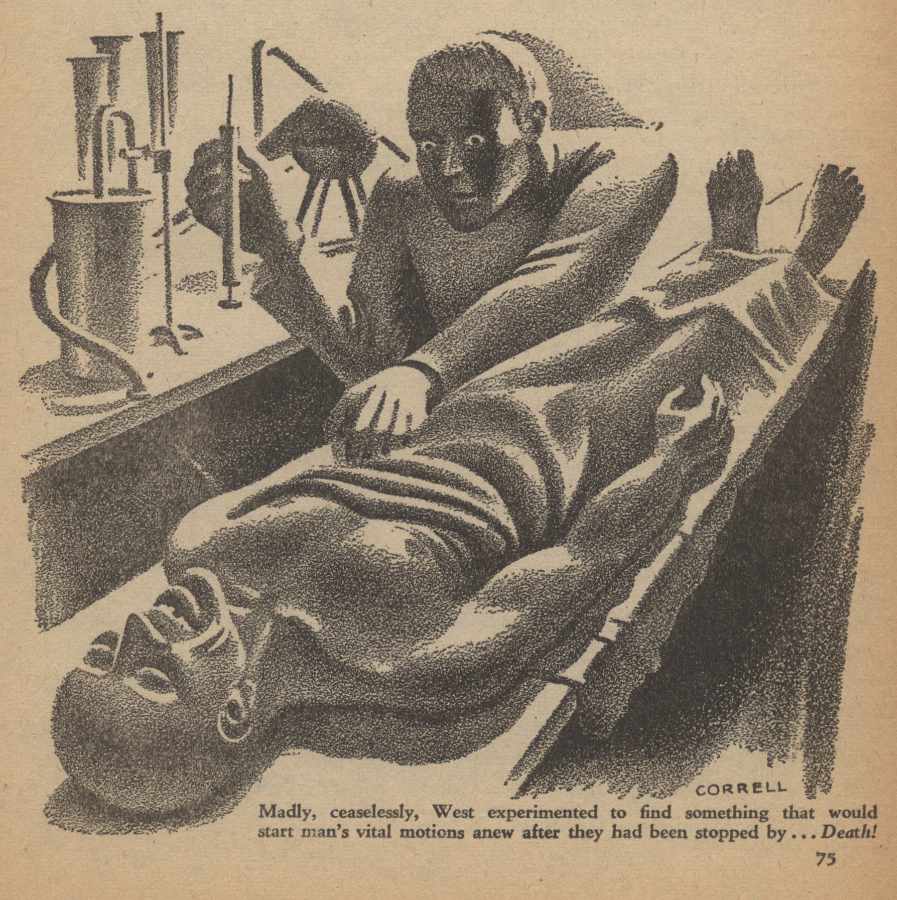
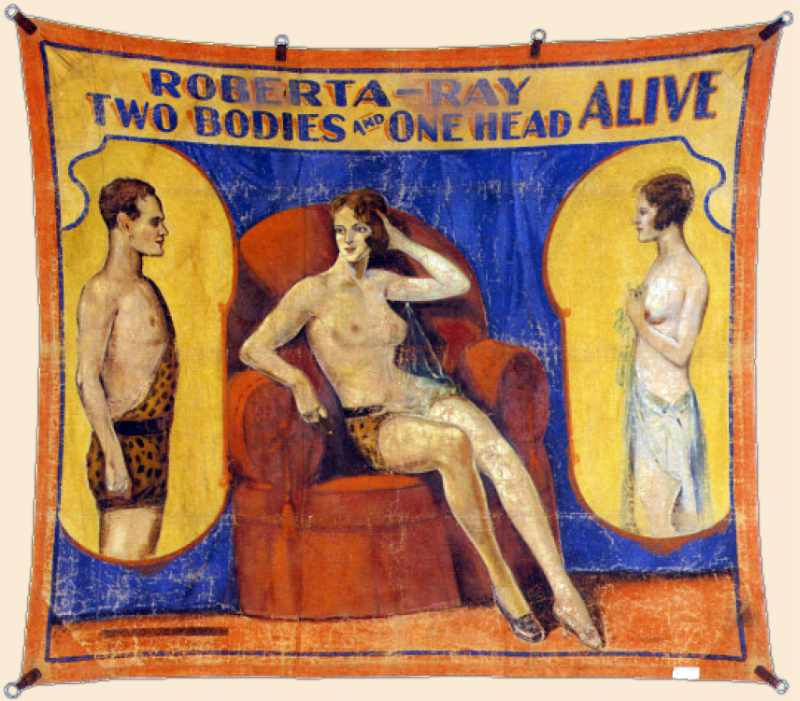
| Description Between 1914 and 1937, American pulp magazines provided a century’s worth of artistic eras on the same newsstand. Pulps still carried the DNA of 19th-century Romanticism, as in the work of Edgar Rice Burroughs. Stories relied on tropes from the Victorian Age in procedural detective stories, as well as the Belle Époque’s Martian queens, gentleman thieves, and masked terrorists. But Modernism also emerged. In literature, Joyce’s Ulysses parodied Homer’s Odyssey mythmaking, and T. S. Eliot’s The Waste Land critiqued the Grail legend. In pop media, H. P. Lovecraft focused on cosmic horror, existential alienation, and multiple perspectives, Metropolis married a descent into industrialized authoritarianism with subjective hallucinations, and Dashiell Hammett invested moral ambiguity, terse, satirical patter, and cynical realism into the hardboiled Continental Op and Sam Spade.
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, performing arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and social issues were all aspects of this movement. Modernism centered around beliefs in a “growing alienation” from prevailing “morality, optimism, and convention” and a desire to change how “human beings in a society interact and live together”. The modernist movement emerged during the late 19th century in response to significant changes in Western culture, including secularization and the growing influence of science. It is characterized by a self-conscious rejection of tradition and the search for newer means of cultural expression. Modernism was influenced by widespread technological innovation, industrialization, and urbanization, as well as the cultural and geopolitical shifts that occurred after World War I. Artistic movements and techniques associated with modernism include abstract art, literary stream-of-consciousness, cinematic montage, musical atonality and twelve-tonality, modern dance, modernist architecture, and urban planning… ~ Modernism – Wikipedia
|